WILDLIFE REFUGE
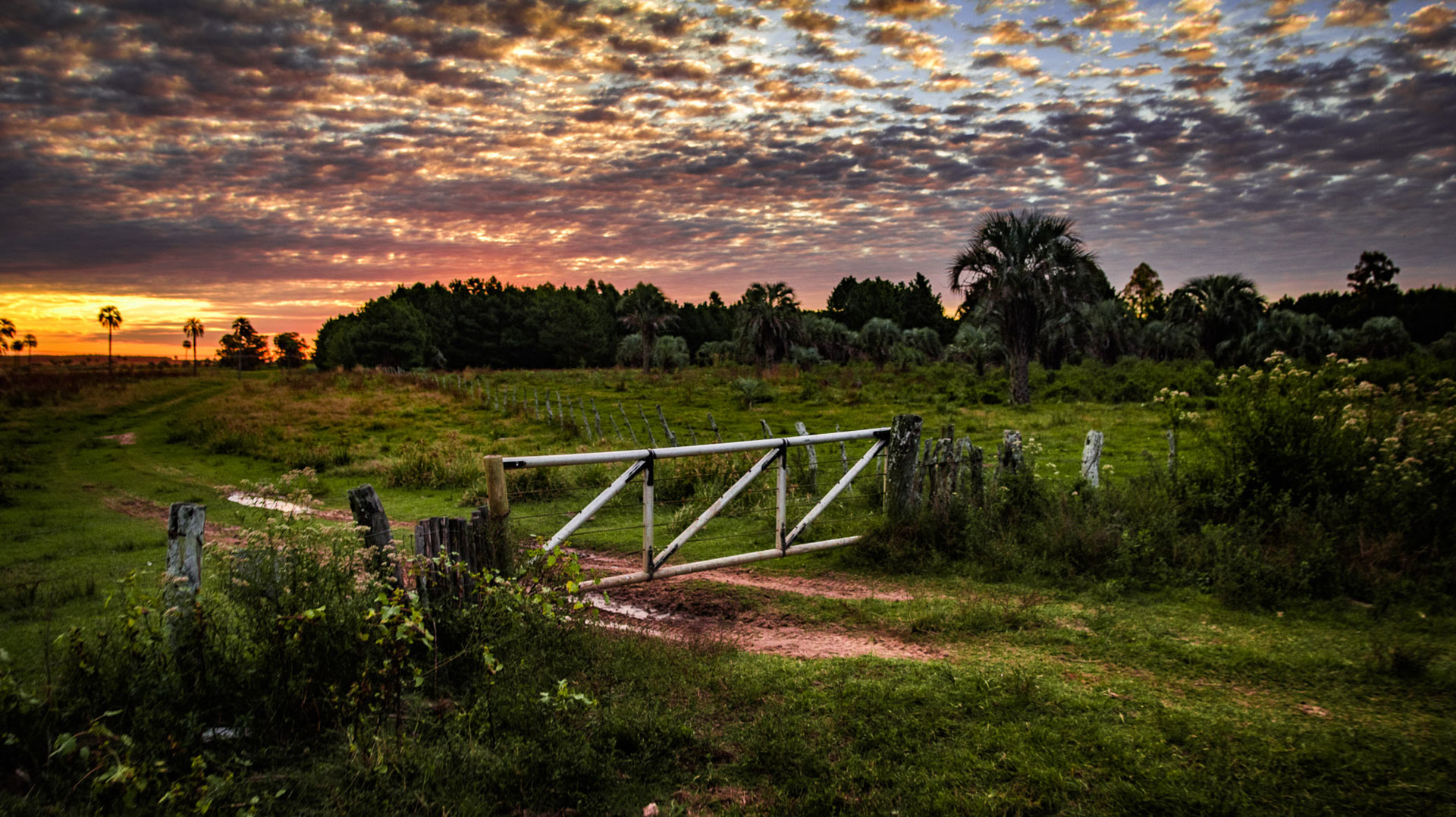
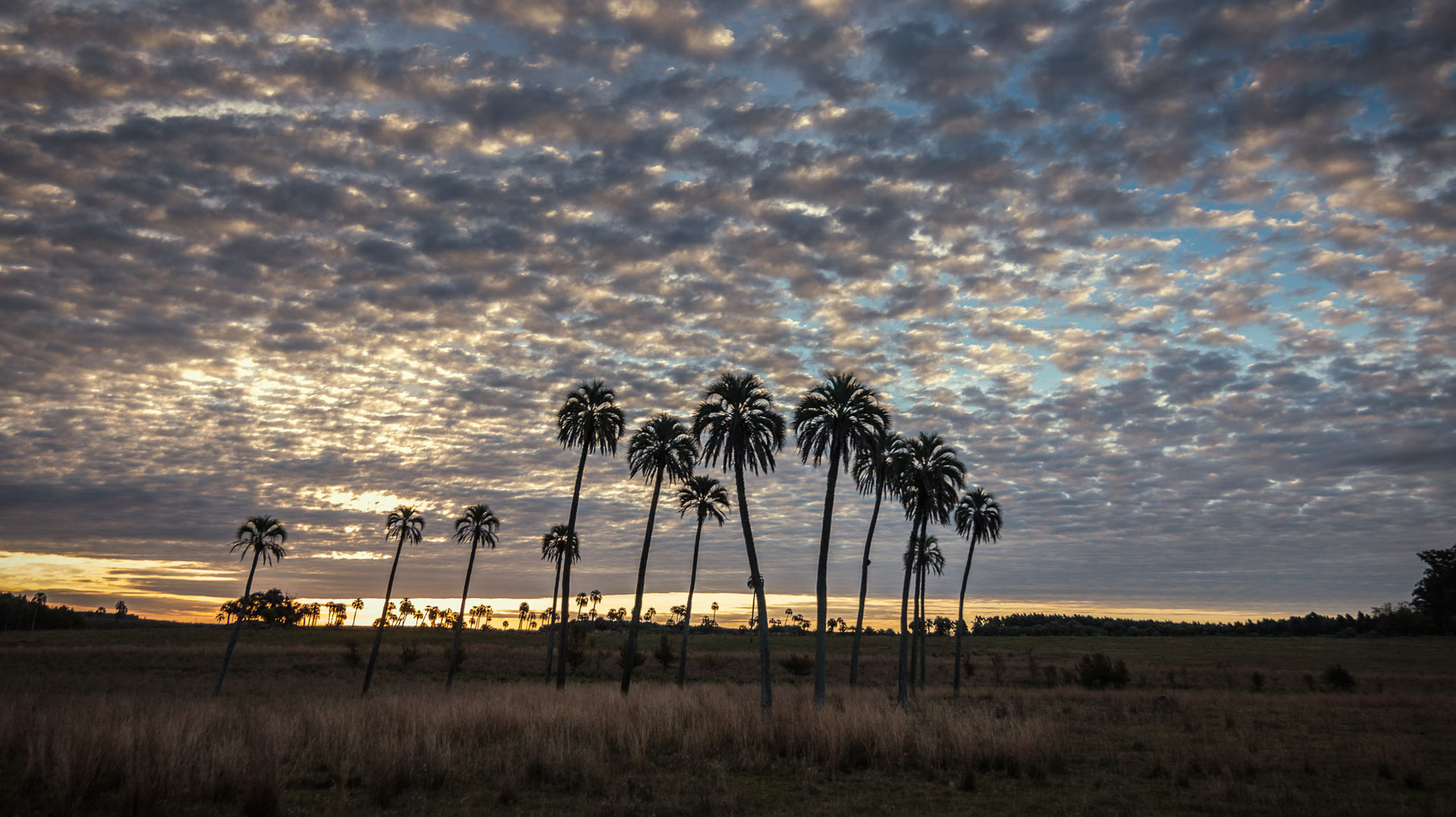
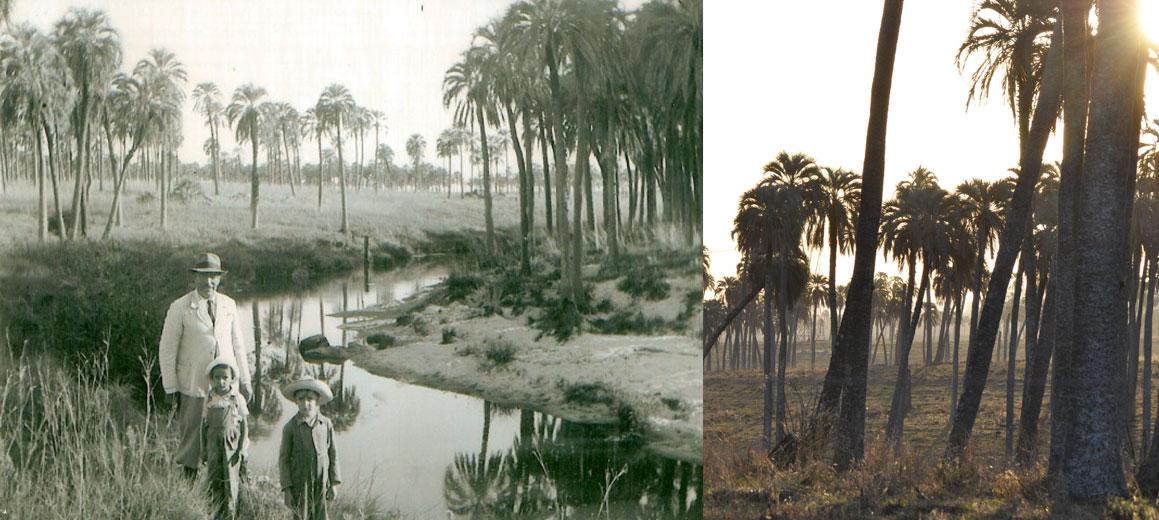
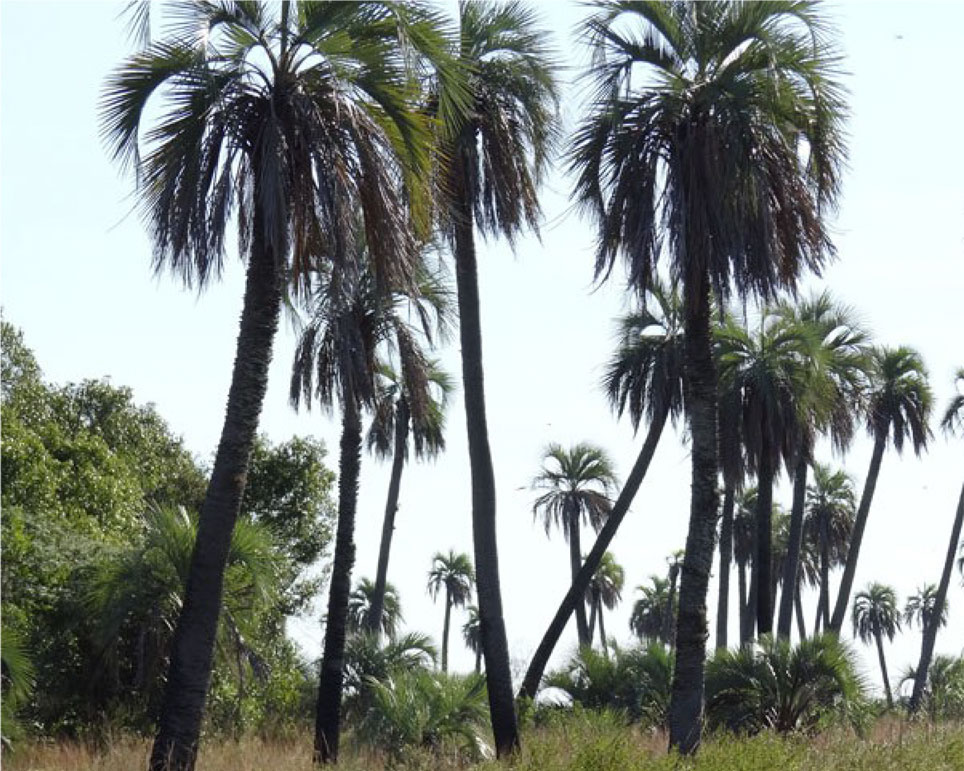
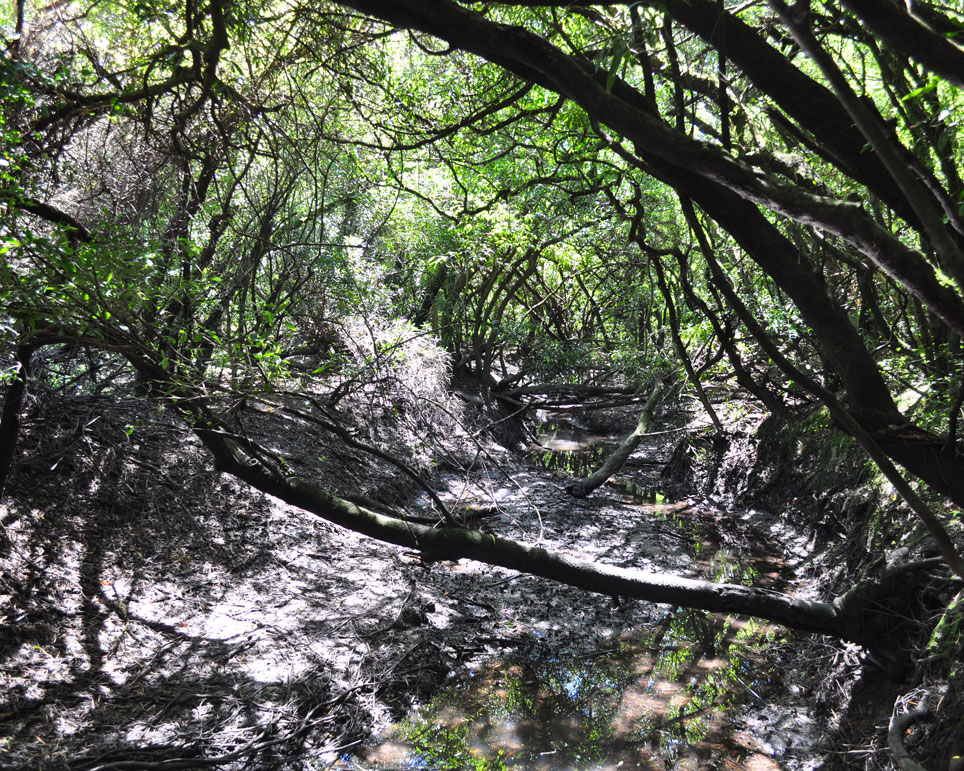
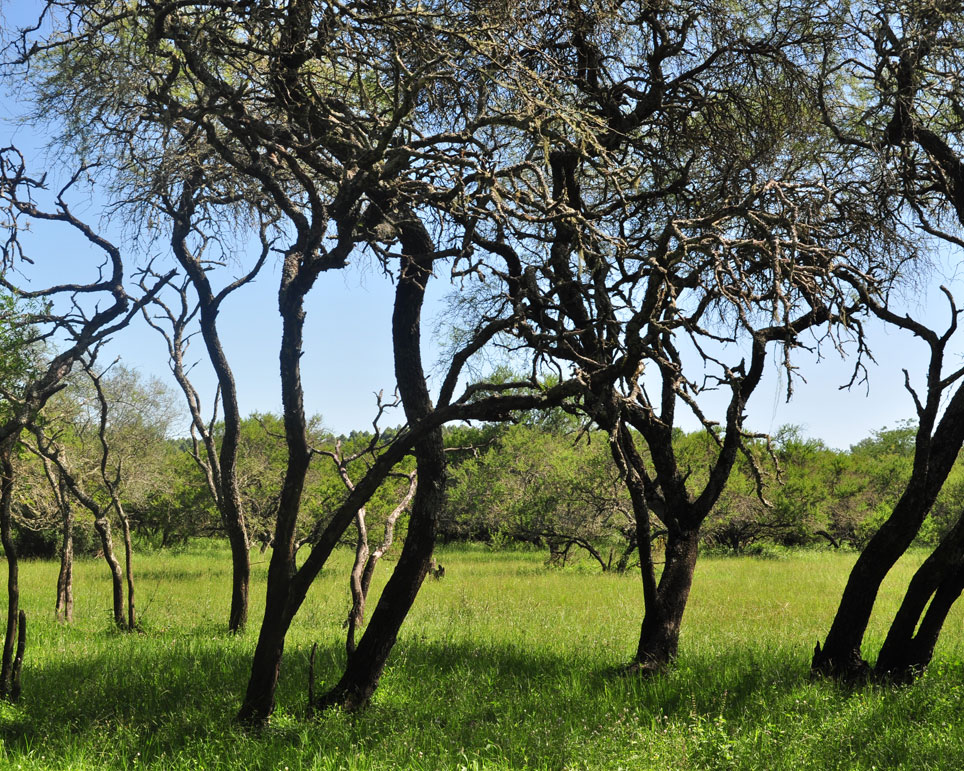
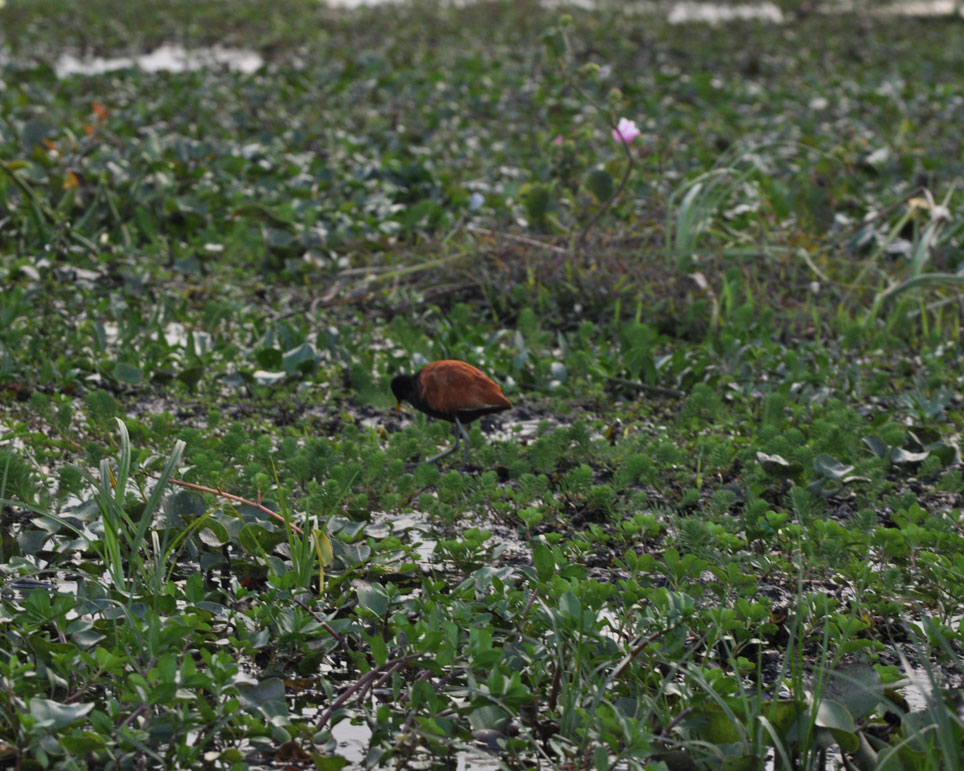
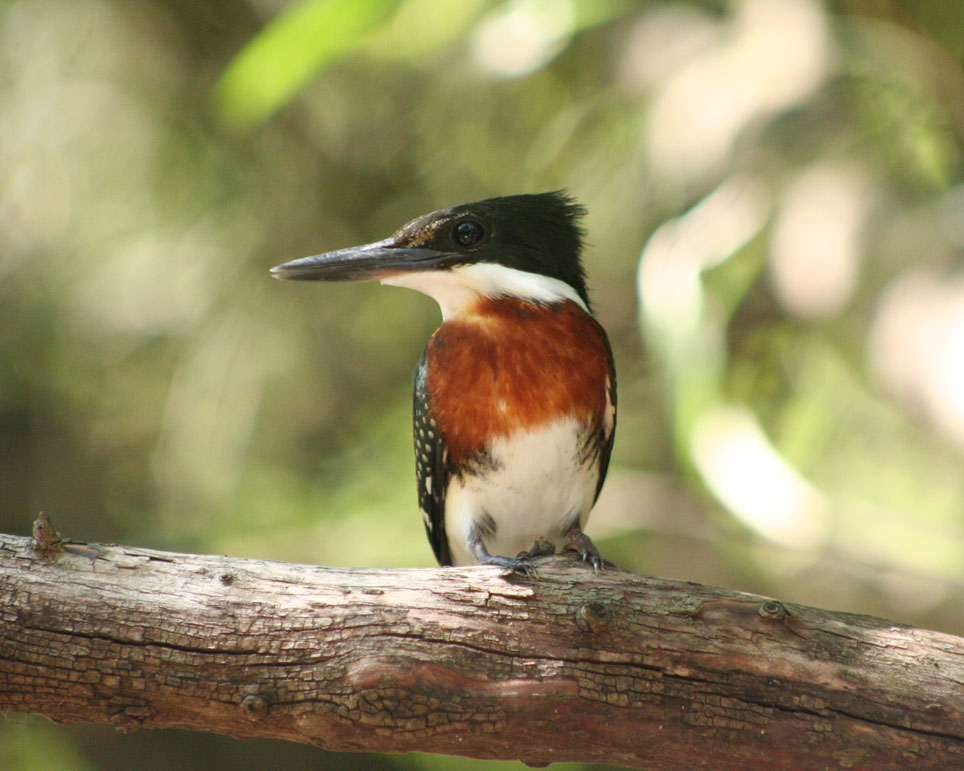
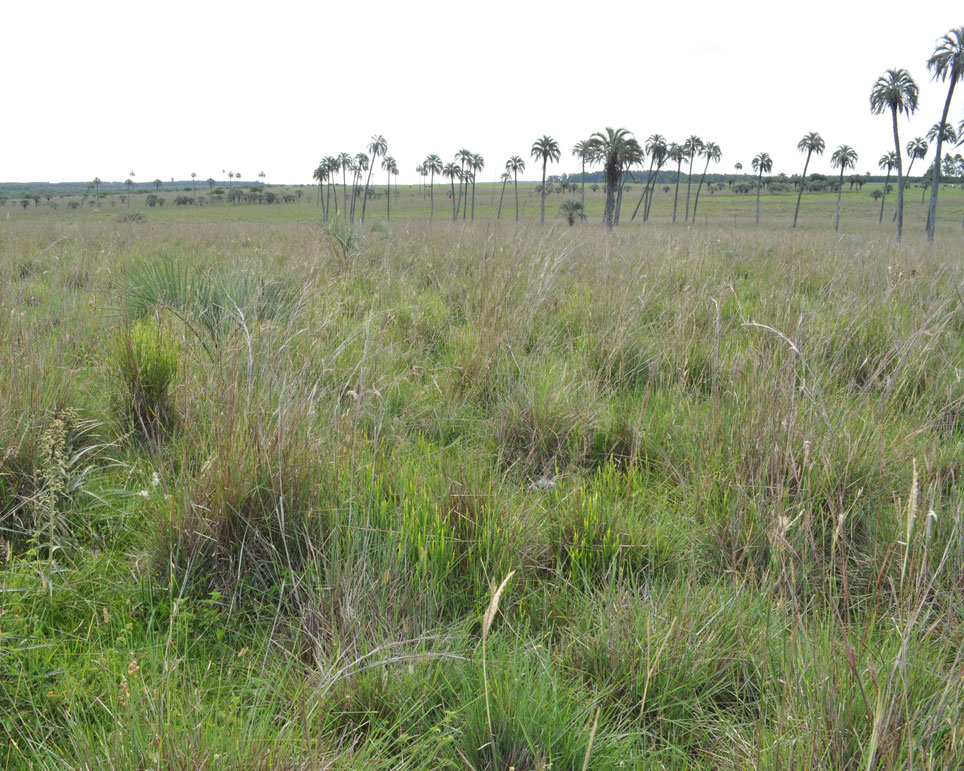
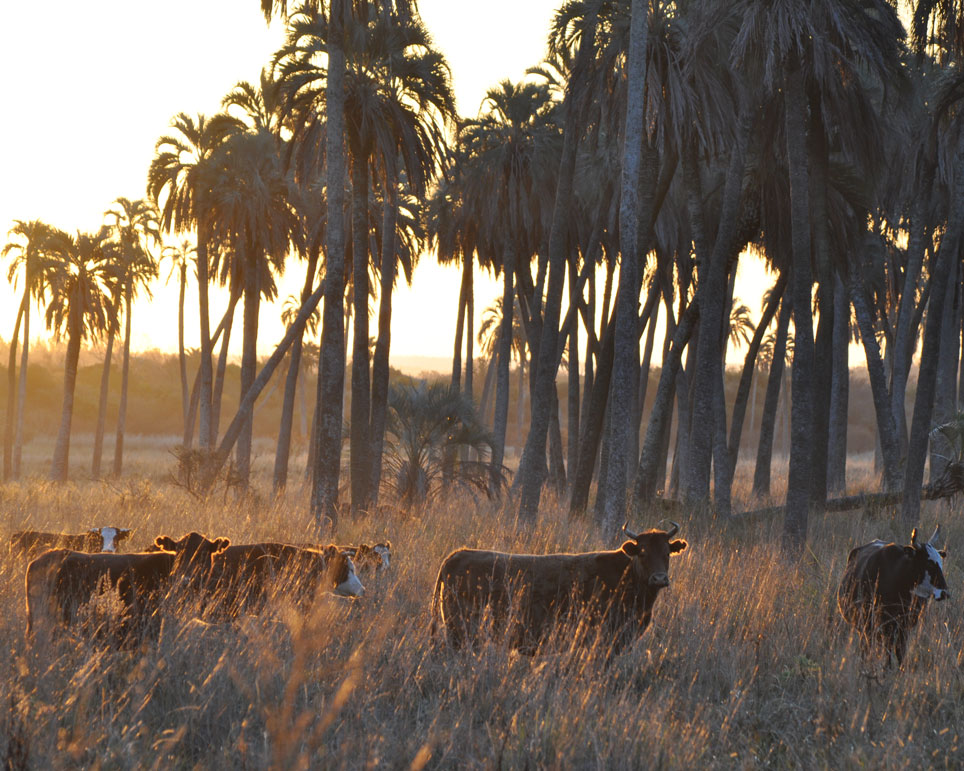
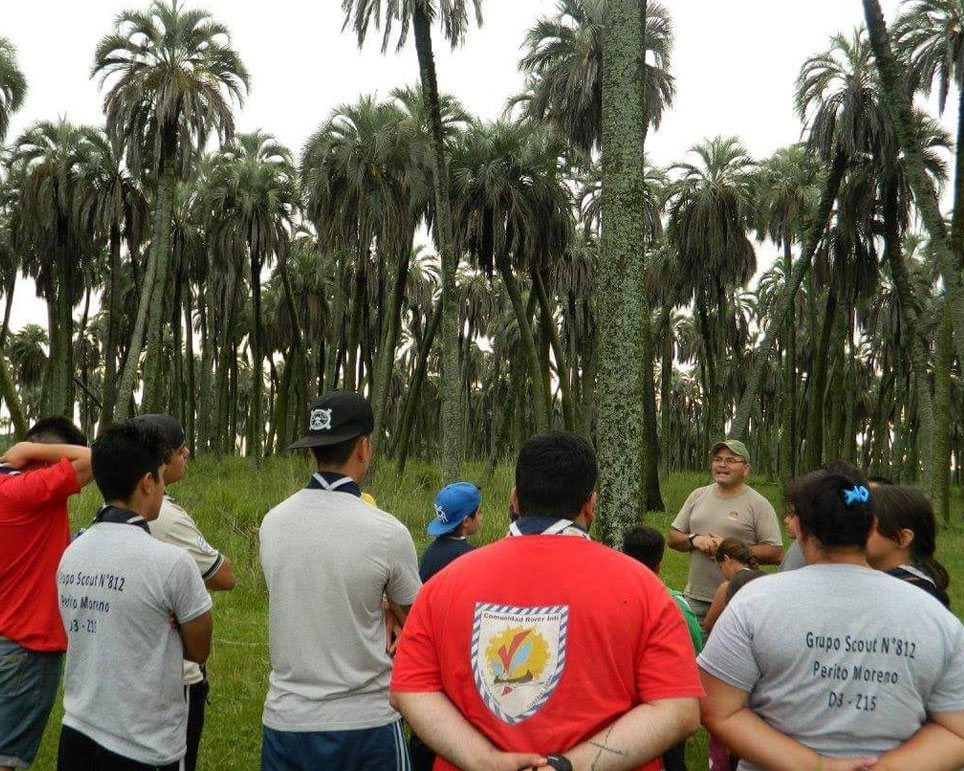
La Aurora del Palmar is located right opposite El Palmar National Park, sharing its natural and topographical characteristics. The area, covering a total of 1,500 hectares, includes 200 ha of healthy 300-year old palm trees, riparian vegetation alongside El Palmar stream, natural grasslands, xerophytic forests, seasonal lagoons and wide range of bird species.
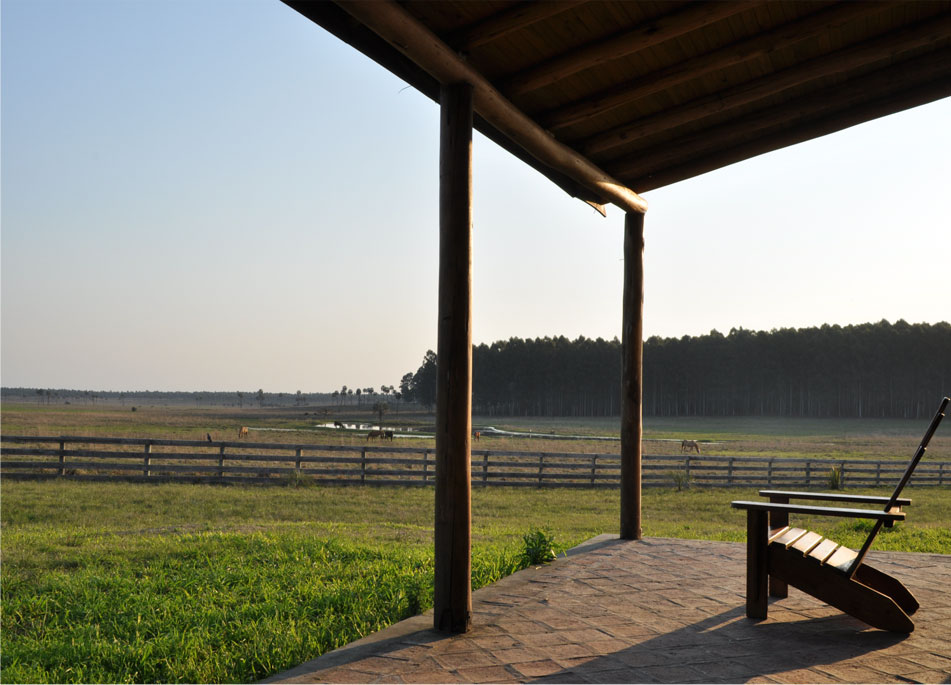
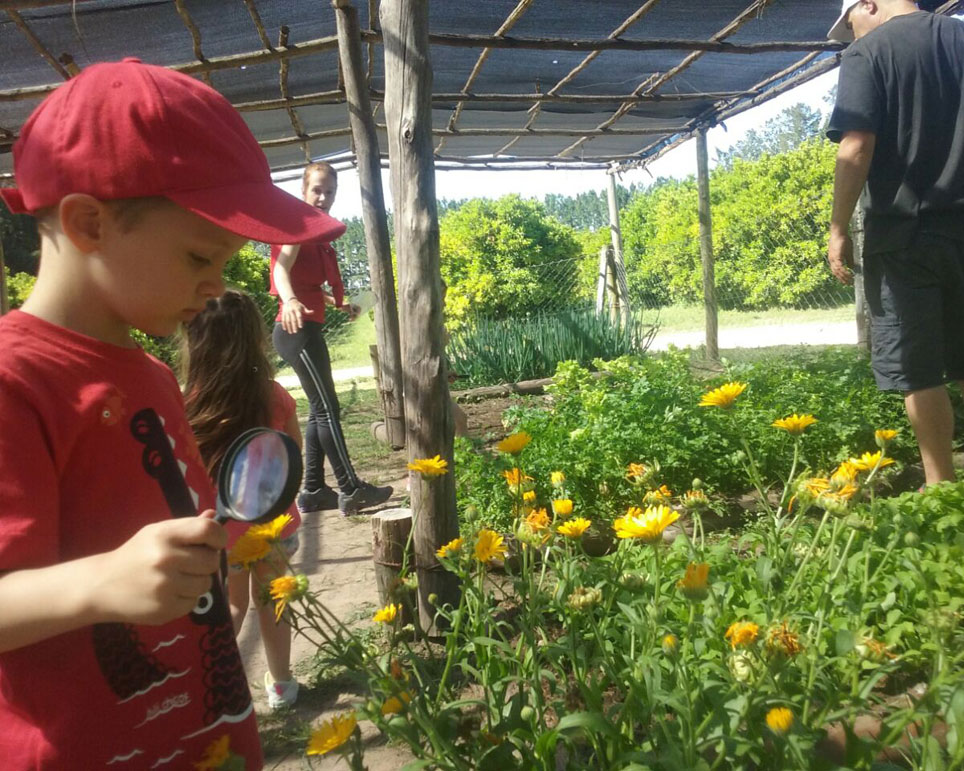
Since 1998, this land of ecological wealth, a wide diversity of native fauna and strategic location has benefited from the assessment of Fundación Vida Silvestre Argentina; the only existing natural reserve in Entre Ríos to receive such benefit. In November 2001, this private property was declared a Multiple Use Natural Reserve by a Decree-Law passed in the province of Entre Ríos. Aurora del Palmar Wildlife Refuge welcomes visitors of all ages and invites them to discover and appreciate these unique environments through ecotourism activities and to enjoy a memorable experience in full contact with nature, always focused on minimizing human impact on the environment.